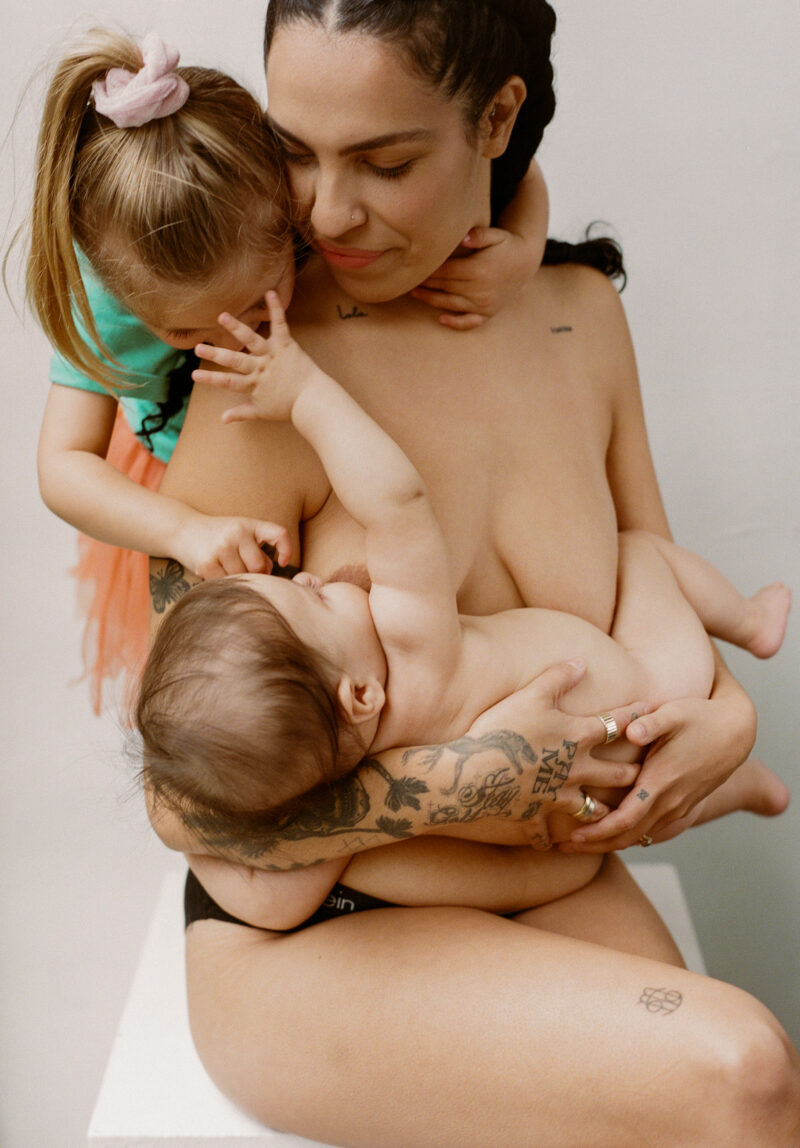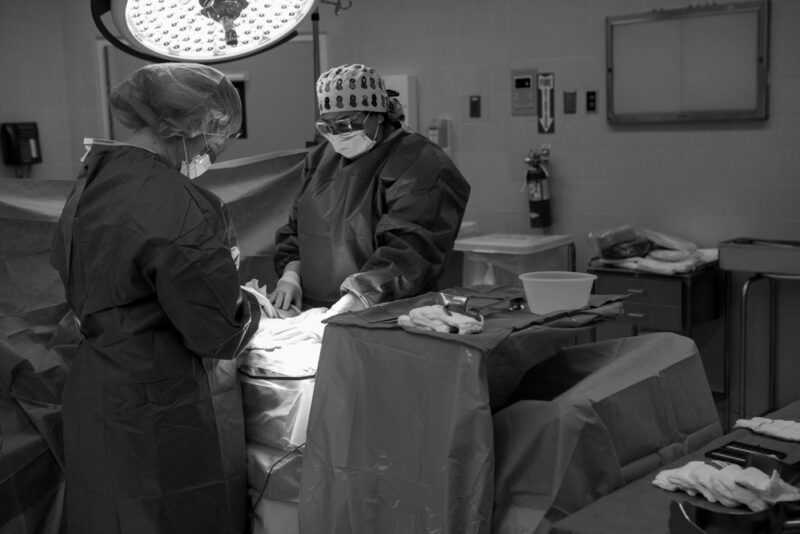
Full spectrum, collaborative care
to support your health and pregnancy goals
Care with Moxie
Birth with Moxie
Care with Moxie
Birth with Moxie
Care with Moxie
Birth with Moxie
Care with Moxie
Birth with Moxie
Care with Moxie
Who we are
Obstetric excellence and the wisdom of midwifery
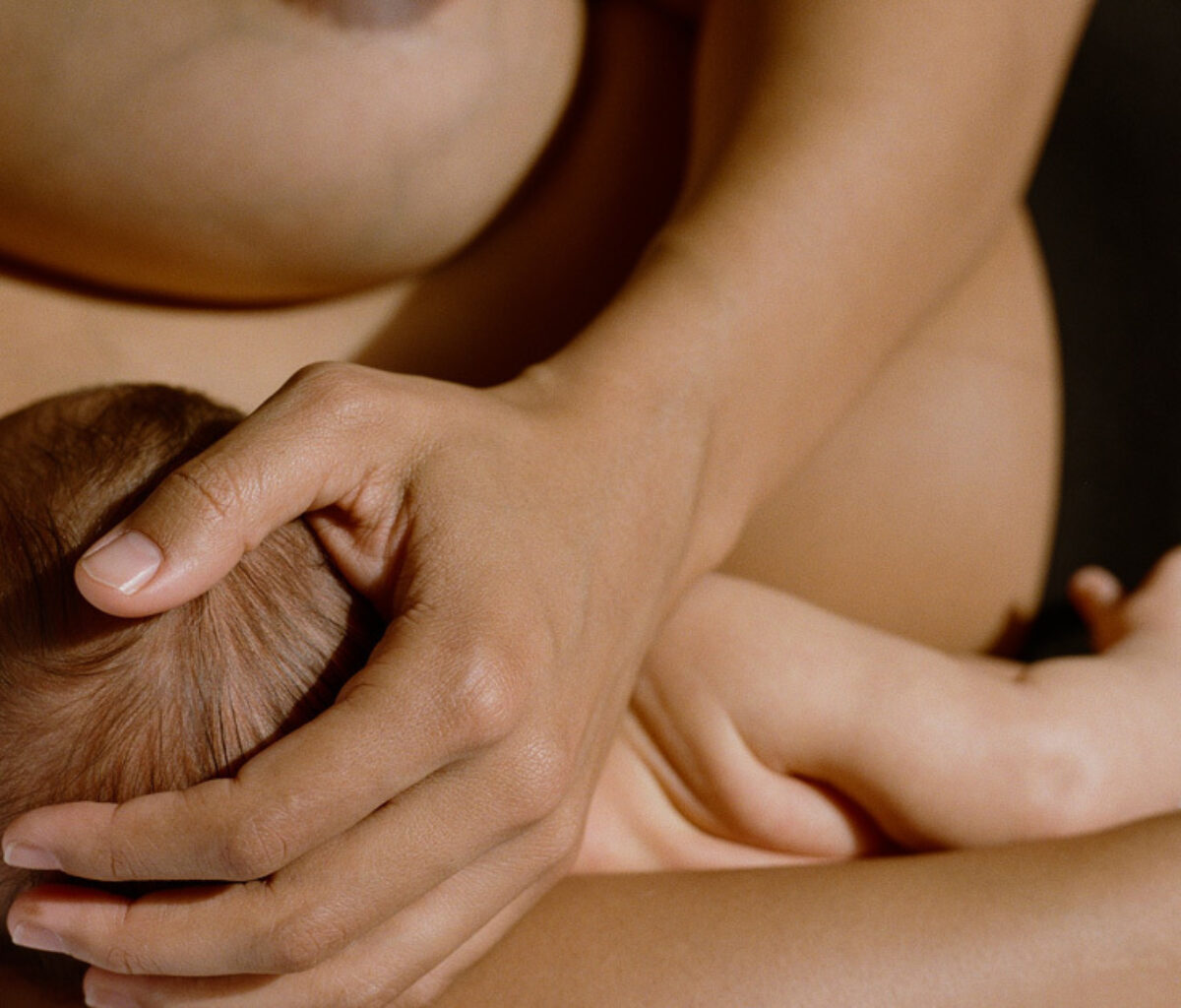
We are a team of midwives and OBGYNs working hand-in-hand to provide personalized, evidence-based, whole person healthcare for all people and families.
We offer a holistic approach to hospital and out-of-hospital birth and compassionate, respectful care across the life span.
Comprehensive client-centered care, with Moxie
Book a consultationWhat we do
Honoring the magic of the human body and the tools that science has afforded us
Access to information
Evidence-based options
Feeling truly seen
Holistic wellbeing
On your terms
Our Reviews
We’re here for our amazing clients, now hear from them
"My dream is for all birthing people to have the care and experience that we had with Dr. Ray. She honored our wants and needs making us feel safe and supported. Labor was very long and intense and Dr. Ray was like this warm light guiding us toward the birth. In my moments of doubt she made me feel heard and seen. Watching Dr. Ray orchestrate the birth felt like this collaborative piece of art and it was truly magical. 10/10 would do it again!"
Michelle J., Hospital Birth"Dr. Bente Kaiser is experienced and compassionate. I wish all my doctors were like her. I'm telling all my friends and family about her. They even gave me snacks and juice when I was done. I felt like a little kid lol but tbh it just made me feel that much more cared for. Being a Black woman, it can be very scary going to the doctor. I truly felt like Dr. Bente Kaiser and staff genuinely cared about me and my comfort for my entire visit."
Chanelle D, IUD removal & replacement"I delivered our second baby 10 minutes after I started pushing! It was magical: our son had delayed cord clamping for over 2 hours, we were nestled in bed cuddling skin-to-skin from the second he arrived, and he was cooed over and adored during every moment of his newborn checkup. I could focus completely on enjoying my newborn and coming back into my body after labor while the team checked me, cared for me, and served me warm breakfast from a local bakery (yes, this actually happened)!"
"I cannot say enough good things about the care I received from Dr. Kaiser and her wonderful team. They took incredible care of me and by baby throughout a very difficult high-risk pregnancy, and always made me feel heard and safe. Dr. Kaiser, Sara, and the wonderful nurses and staff here truly deliver excellent, equitable, and accessible care with equal parts compassion and skill."
Christie W, High-risk pregnancy care"Sara Howard performed my Pap smear today and I have never felt so safe and heard by a doctor in my life. I have regularly seen a gynecologist for 10 years now and not one of them has listened to my concerns or gotten me proper testing beyond a standard exam. Finally, after all this time I'm going to get the answers I've been looking for. I can't thank her enough for listening to me and understanding that a patient knows their own body."
Tessa P, Cervical cancer screening"Dr. Kaiser delivered both of my daughter…she worked with me to have the unmedicated births I'd planned for (she's amazing at making that happen in a hospital setting), and has had the uncanny ability to say the exact thing I needed to hear during the hardest parts of labor to keep me focused and calm and empowered to get through it."
OUR EXPERTS
Meet your team
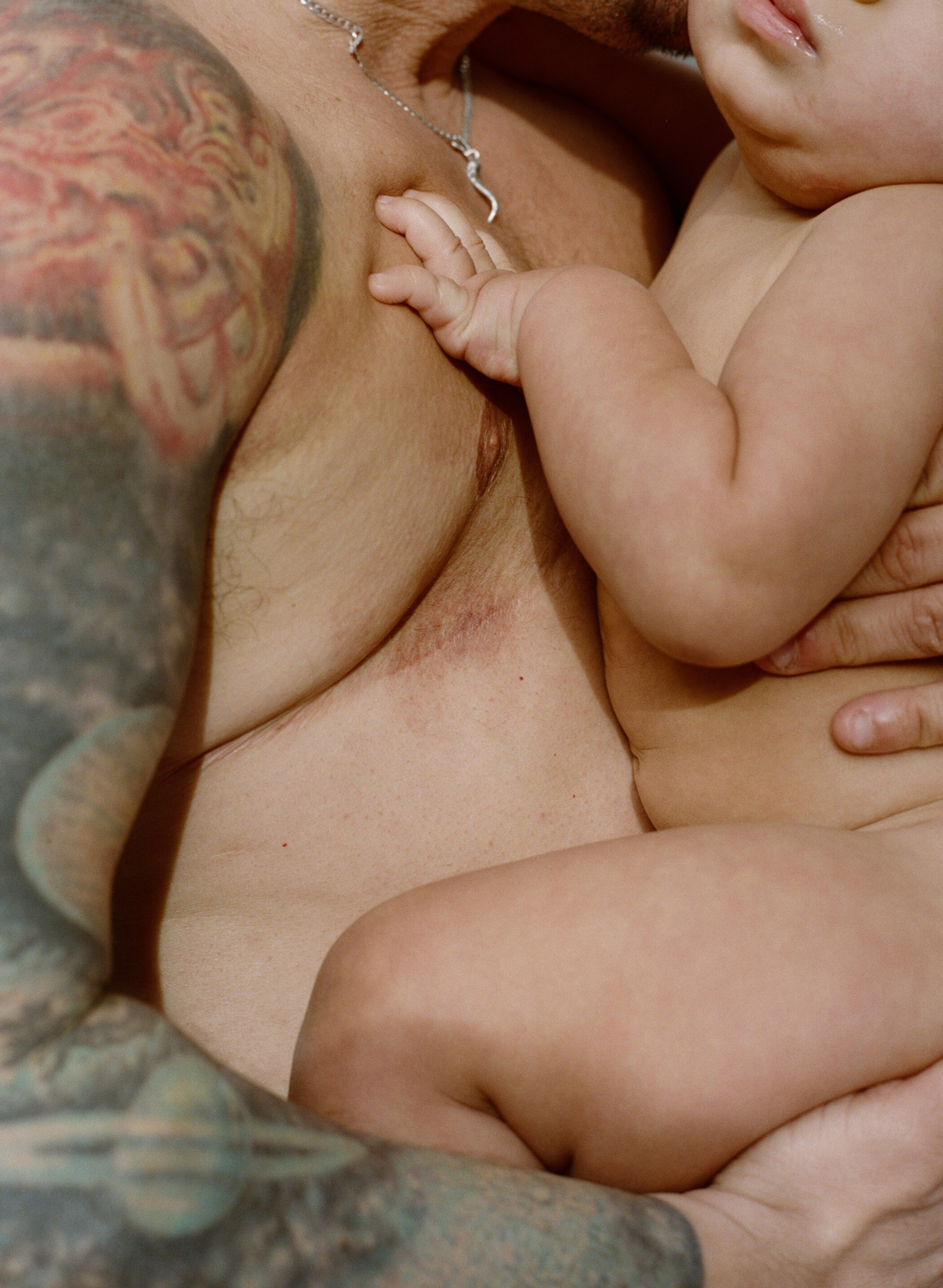

No two bodies are the same
No two journeys are the same
There are many ways to be well
Collaboration with expertise
Choosing is your right




BOOK A CONSULTATION
Personalized, integrative care that supports you on your unique journey